Today is March 17th, 2015 and I'd like to welcome you to this webinar on resolving 941 tax debts. My name is Jason Bowman from tax marketing hq.com and for the next 15 minutes, we're going to be discussing the special situations involved in resolving 941 tax liabilities. We will also be exploring why these liabilities are such a huge enforcement priority for the IRS and how you can help your clients with their employment tax problems. Additionally, we will be assessing specific penalties and appeals options related to 941 taxes. It's important to note that we cannot discuss the 941 landscape without also talking about the trust fund every penalty. The trust fund recovery penalty itself deserves extensive attention, so I will be doing another webinar in the future specifically focused on trust fund issues. Now, let's quickly touch on the penalties. The first ones are the failure to file and failure to pay penalties. The failure to file penalties accumulate at a rate of 5% per month, capping at 25%. There is also a minimum penalty of $135 or 100% of the tax due, whichever is less. The failure to pay penalty is in addition to the federal tax deposit penalty, which is 0.5% per month with a 25% cap. It's important to remember that the 25% cap applies to the aggregate of both penalties. Furthermore, employment tax situations come with the specific federal tax deposit penalty. This penalty scales rapidly and provides insight into why employment taxes are a significant concern for the IRS. For monthly depositors or semi-weekly depositors, the penalty rate varies depending on the lateness of the deposit. If the deposit is between 1 and 5 days late, the penalty is only 2%. If it's between 6 and 15 days late, the penalty increases...
Award-winning PDF software





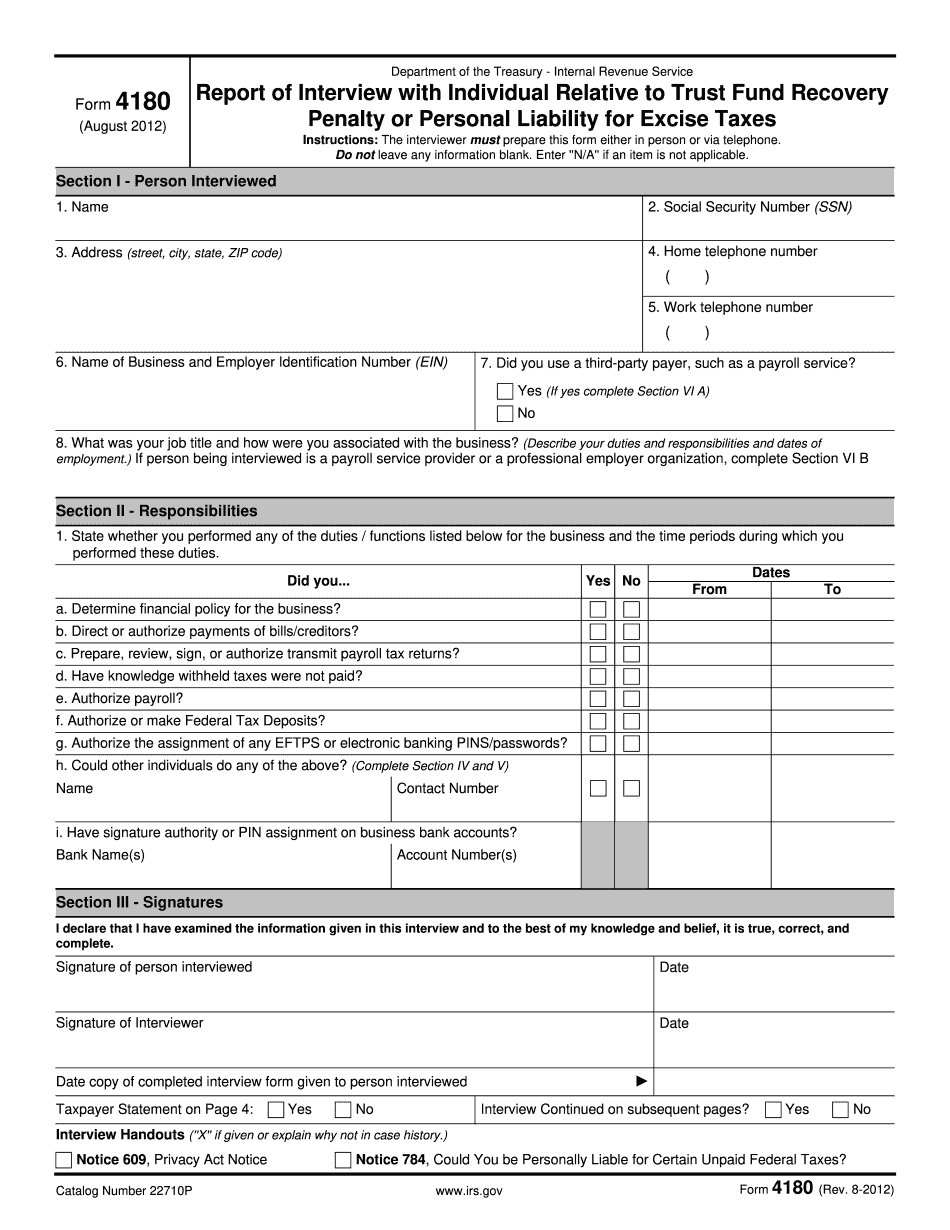
Unpaid trust fund taxes Form: What You Should Know
IRS Trust Fund Recovery Penalty — Employer Payments (Form 941) The trust fund recovery penalty is a sum of two parts: the balance of a tax liability and the penalty. The penalty is equal to the balance of the taxpayer's tax liability. To determine the penalty, the IRS looks at the total amount of tax with respect to the tax period in question. This part of the penalty can be significant, and you may be required to compensate the employer for any employer payments (Form 941) that your employees paid to you. The penalty is 100 per employee per tax period if unpaid for 1 year, 500 per employee per tax period if unpaid for 2 years, and increases with each payment. It can be a very substantial sum of money! Tax Deduction The trust fund recovery penalty can add to your tax due and can result in additional penalties, penalties on tax increases (Rate increases), and/or interest. The penalties for withholding (Form 941) and taxes collected (Form 941-EZ) are the same for income tax and Social Security taxes. In order to mitigate those penalties, it is necessary to properly file IRS Form 8606, Schedule EZ, each year and report any interest or penalties as a regular part of your income tax return. If the IRS collects the trust fund tax through an employer withholding, it is considered to have been paid by the employee. The trust fund recovery penalty is not taken into account in the calculation of the federal income tax due on employer withholding. The Trust Fund Recovery Penalty — Interest and Penalty on Late Filing The penalty amount is interest, which is 1% per month of the penalty amount, starting on the due date of each pay period and ending on the 30th day following the due date of your income tax return. You may incur penalties if you fail to make your tax returns on or before the due date. Penalty interest accrues the earlier the return is not filed. The penalty is not reduced by any amounts withheld during that period. You may incur penalties on penalties due to errors made on your return. The penalty amount is due and payable when the return has been filed, no later than 7 years after the calendar tax year for which the recovery is sought. If it has been 6 months since the return was filed, the penalty period for that year begins on the due date, regardless of when the deficiency or tax was actually paid.
online solutions help you to manage your record administration along with raise the efficiency of the workflows. Stick to the fast guide to do Form 4180, steer clear of blunders along with furnish it in a timely manner:
How to complete any Form 4180 online: - On the site with all the document, click on Begin immediately along with complete for the editor.
- Use your indications to submit established track record areas.
- Add your own info and speak to data.
- Make sure that you enter correct details and numbers throughout suitable areas.
- Very carefully confirm the content of the form as well as grammar along with punctuational.
- Navigate to Support area when you have questions or perhaps handle our assistance team.
- Place an electronic digital unique in your Form 4180 by using Sign Device.
- After the form is fully gone, media Completed.
- Deliver the particular prepared document by way of electronic mail or facsimile, art print it out or perhaps reduce the gadget.
PDF editor permits you to help make changes to your Form 4180 from the internet connected gadget, personalize it based on your requirements, indicator this in electronic format and also disperse differently.
Video instructions and help with filling out and completing Unpaid trust fund taxes